Choosing Cloud or Starlink: Navigating Global Connectivity
In today’s interconnected world, reliable and ubiquitous connectivity is paramount. Choosing between cloud computing and Starlink for global connectivity can be a daunting task, but this guide will help you navigate the key considerations to make an informed decision.
Cloud computing offers a vast network of data centers, providing scalable and cost-effective solutions. Starlink, on the other hand, utilizes a constellation of low-earth orbit satellites to deliver high-speed internet to remote and underserved areas.
Latency and Connectivity: Choosing Between Cloud Computing And Starlink For Global Connectivity
Latency, the time it takes for data to travel between two points, is crucial for many applications. Cloud Computing, with its centralized data centers, typically has higher latency compared to Starlink’s low-earth orbit satellites. This latency difference can significantly impact applications requiring real-time responsiveness, such as video conferencing, gaming, and remote control.
Advantages of Starlink’s Low-Earth Orbit Satellites
*
-*Lower latency
Starlink’s satellites are positioned closer to Earth, reducing the distance data must travel, resulting in lower latency.
-
-*Increased bandwidth
Starlink’s constellation of satellites provides increased bandwidth, enabling faster data transfer rates.
-*Global coverage
Starlink aims to provide global coverage, making it accessible in remote areas where terrestrial internet is unavailable.
Disadvantages of Starlink’s Low-Earth Orbit Satellites
*
-*Cost
When deciding between cloud computing and Starlink for global connectivity, it’s essential to consider future advancements. Starlink, with its planned 2024 satellite internet upgrades ( Starlink 2024 Satellite Internet Advancements ), promises significant enhancements in coverage, speed, and reliability. These advancements may bridge the gap between cloud computing’s global reach and Starlink’s potential for seamless connectivity in remote and underserved areas, offering a more comprehensive solution for global connectivity.
Starlink’s services are currently more expensive than traditional broadband internet.
-
-*Weather dependency
Starlink’s satellites are susceptible to weather conditions, which can affect connectivity.
-*Limited capacity
Starlink’s satellites have limited capacity, which may result in congestion during peak usage times.
Cost Considerations
When comparing Cloud Computing and Starlink for global connectivity, cost is a crucial factor to consider. Both options have distinct pricing models, and the long-term cost implications vary depending on usage patterns and geographic location.
Pricing Models
Cloud Computing typically follows a pay-as-you-go model, where users are charged based on the resources consumed, such as storage, compute, and bandwidth. Starlink, on the other hand, has a subscription-based pricing model, with a monthly fee that includes a certain amount of data usage.
Long-Term Cost Implications
For low data usage, Starlink’s subscription model can be more cost-effective than Cloud Computing. However, as data usage increases, Cloud Computing’s pay-as-you-go model becomes more economical.
Factors Affecting Costs
- Data Usage:Higher data usage leads to higher costs for Cloud Computing but not for Starlink within the subscription limit.
- Geographic Location:Cloud Computing costs can vary depending on the location of the data center, while Starlink’s costs are generally consistent globally.
Reliability and Availability
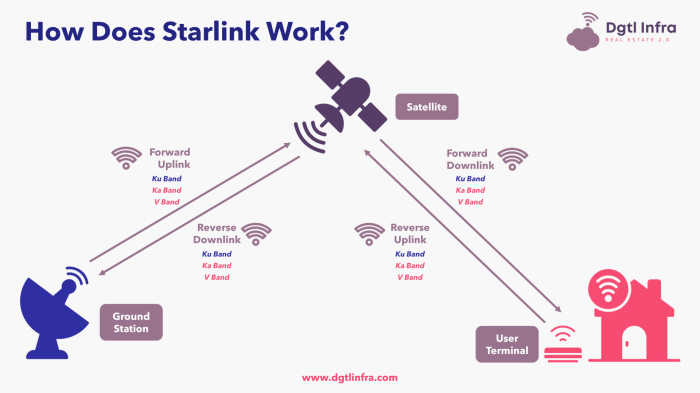
Cloud Computing providers typically offer high levels of reliability and uptime guarantees, with service level agreements (SLAs) that define the expected performance and availability of their services. These guarantees are backed by redundant infrastructure, multiple data centers, and robust disaster recovery plans.
However, even with these measures in place, outages and disruptions can still occur, especially during major events or natural disasters.
Potential Risks and Vulnerabilities
Cloud Computing services can be vulnerable to cyberattacks, such as distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks, which can overwhelm servers and disrupt availability. Additionally, data breaches and security incidents can compromise the integrity and confidentiality of data stored in the cloud.Starlink, on the other hand, is designed to provide resilient connectivity even in remote and challenging environments.
Its satellite network is less susceptible to terrestrial disruptions, such as power outages or cable cuts. However, weather conditions, such as heavy rain or snow, can impact signal strength and availability. Additionally, the limited number of satellites in orbit can create bottlenecks during peak usage times, leading to slower speeds or reduced connectivity.
When it comes to global connectivity, the choice between cloud computing and Starlink is a crucial one. While cloud computing offers reliable and scalable solutions, Starlink’s upcoming advancements, as detailed in the article Revolutionizing Global Connectivity with Starlink 2024 , promise to transform the landscape.
By leveraging the power of low-earth orbit satellites, Starlink aims to provide seamless and affordable internet access to even the most remote areas. This breakthrough has the potential to reshape the way we approach global connectivity, and it will be fascinating to see how it compares to the established cloud computing models in the years to come.
Geographic Constraints
The availability of both Cloud Computing and Starlink services can be affected by geographic constraints. Cloud Computing data centers are typically concentrated in major metropolitan areas, while Starlink’s satellite coverage is still expanding. As a result, organizations in remote or underserved areas may have limited access to these services or experience higher latency and lower speeds.
Data Security and Privacy

Data security and privacy are paramount concerns when choosing between Cloud Computing and Starlink. Cloud Computing providers implement robust security measures, including encryption, access controls, and regular security audits. Starlink, on the other hand, relies on end-to-end encryption and a distributed network architecture to enhance data protection.
Potential Risks and Threats to Data Privacy, Choosing Between Cloud Computing and Starlink for Global Connectivity
In Cloud Computing, data is stored on centralized servers, making it a potential target for hackers and cyberattacks. Starlink’s distributed network architecture reduces this risk by eliminating single points of failure.
When evaluating options for global connectivity, it’s essential to consider the evolving landscape of satellite internet technology. Starlink 2024 promises advancements that could significantly impact the choice between cloud computing and satellite-based solutions. Understanding these advancements can help businesses make informed decisions about their global connectivity strategies.
Recommendations for Mitigating Data Security Concerns
- Encryption:Encrypt data at rest and in transit to prevent unauthorized access.
- Access Controls:Implement strict access controls to limit who can access data.
- Regular Security Audits:Conduct regular security audits to identify and address vulnerabilities.
- Data Backup:Maintain regular data backups to ensure data recovery in case of a breach.
Scalability and Flexibility
Cloud computing and Starlink offer varying degrees of scalability and flexibility, enabling businesses to adapt to changing bandwidth requirements and usage patterns.
Cloud Computing
Cloud computing provides on-demand scalability, allowing businesses to quickly provision or deprovision resources as needed. This flexibility is particularly beneficial for organizations with fluctuating workloads or seasonal demand spikes. Cloud providers offer a range of instance types and configurations, allowing businesses to tailor their infrastructure to specific application requirements.
Starlink
Starlink offers flexibility through its satellite constellation, which provides global coverage and can be scaled up or down to meet changing demand. Starlink’s low-earth orbit satellites can be deployed or repositioned as needed, enabling businesses to adjust their connectivity in response to changing market conditions or geographic expansion.
Final Thoughts

Ultimately, the choice between cloud computing and Starlink depends on your specific needs and priorities. By carefully weighing the factors discussed in this guide, you can make an informed decision that will optimize your global connectivity and drive your business forward.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the key differences between cloud computing and Starlink?
Cloud computing relies on data centers, while Starlink utilizes satellites. Cloud computing offers scalability and cost-effectiveness, while Starlink provides high-speed internet in remote areas.
How does latency impact the choice between cloud computing and Starlink?
Latency is the time it takes for data to travel between devices. Cloud computing typically has lower latency than Starlink due to its proximity to data centers. However, Starlink’s latency is improving rapidly.
What are the cost implications of choosing cloud computing or Starlink?
Cloud computing pricing models vary based on usage, while Starlink offers fixed monthly subscription fees. The cost of cloud computing can be lower for high-bandwidth applications, while Starlink may be more cost-effective for remote locations.