Cloud Diagram Server Security: Enhancing Cloud Security
Cloud diagram server security is paramount in today’s digital landscape, ensuring the protection of sensitive data and maintaining the integrity of cloud-based systems. This comprehensive guide delves into the crucial aspects of securing cloud servers, exploring best practices, architectures, compliance, threat detection, and industry standards.
As businesses increasingly rely on cloud computing, understanding the intricacies of cloud diagram server security becomes essential. This guide provides a roadmap for implementing robust security measures, safeguarding data, and ensuring business continuity in the cloud era.
Server Security Measures
Implementing robust security measures for cloud servers is crucial to safeguard data and prevent unauthorized access. By adhering to best practices, organizations can protect their cloud infrastructure from potential threats.
Best practices for securing cloud servers include:
Firewalls
Firewalls act as a first line of defense by filtering incoming and outgoing network traffic. They allow only authorized traffic to enter or leave the server, blocking malicious attempts and preventing unauthorized access.
Encryption
Encryption scrambles data to make it unreadable to unauthorized individuals. This ensures that even if data is intercepted, it cannot be deciphered without the proper encryption key.
Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS)
IDSs monitor network traffic and server activity for suspicious patterns. They can detect and alert administrators to potential security breaches, allowing for prompt response and mitigation.
Cloud Server Architecture
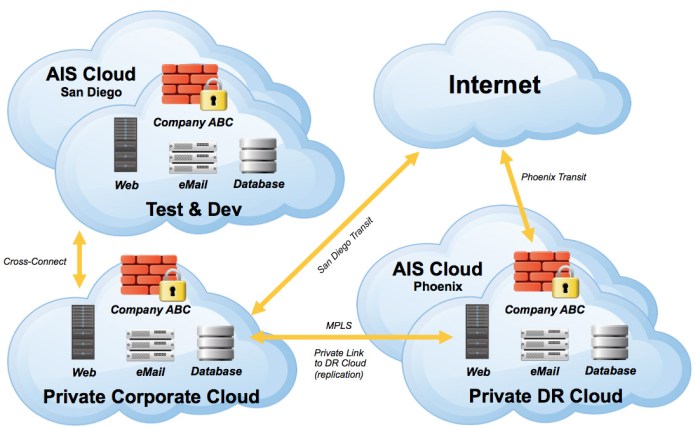
Cloud server architecture refers to the way cloud computing resources are organized and delivered. There are three main cloud server architectures: Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS).
IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service)
IaaS provides the underlying infrastructure, such as servers, storage, and networking, over the internet. Customers have control over the operating system, applications, and data, allowing for greater flexibility and customization. However, IaaS requires a higher level of technical expertise to manage and secure the infrastructure.
PaaS (Platform as a Service)
PaaS offers a platform for developing, deploying, and managing applications without the need to manage the underlying infrastructure. PaaS providers handle the operating system, middleware, and runtime environment, allowing developers to focus on their applications. This reduces complexity and simplifies development, but limits customization and control over the infrastructure.
SaaS (Software as a Service)
SaaS provides access to software applications over the internet. Customers subscribe to the software and use it on a pay-as-you-go basis, without the need to install or manage the software or infrastructure. SaaS is easy to use and requires minimal technical expertise, but offers limited customization and control over the software and data.
Security Considerations, Cloud diagram server security
The choice of cloud server architecture depends on factors such as security requirements, technical expertise, and customization needs. Each architecture has its own security implications:
- IaaSrequires a higher level of security measures as customers are responsible for securing the underlying infrastructure.
- PaaSprovides a more secure environment as the provider manages the infrastructure and platform, but customers still need to secure their applications and data.
- SaaSoffers the highest level of security as the provider is responsible for all aspects of the software and infrastructure.
Cloud Security Compliance
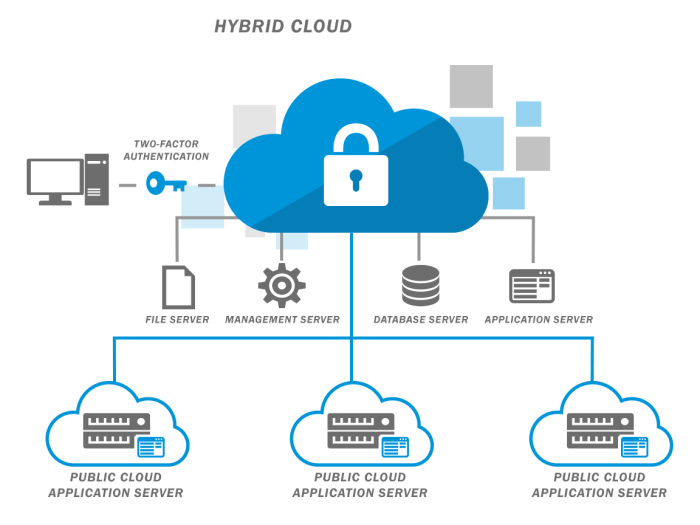
Maintaining compliance with industry security standards and regulations is paramount for cloud servers. Adhering to these frameworks ensures the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of data stored and processed in the cloud.
Compliance frameworks provide a set of best practices and guidelines that organizations can follow to enhance their security posture. By meeting the requirements of these frameworks, organizations can demonstrate their commitment to data protection and reduce the risk of security breaches.
Key Security Compliance Frameworks
Several key security compliance frameworks are widely recognized and adopted by organizations worldwide. These include:
- ISO 27001/ISO 27002:International standards that provide a comprehensive framework for information security management.
- NIST Cybersecurity Framework (CSF):A US-based framework that provides guidance on cybersecurity risk management and incident response.
- HIPAA:US healthcare industry regulations that protect the privacy and security of patient health information.
- PCI DSS:Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard, which sets requirements for organizations that process, store, or transmit credit card data.
- SOC 2:A US-based standard that focuses on the security and availability of cloud services.
Each framework has its own specific requirements and scope. Organizations should carefully evaluate their needs and select the frameworks that are most relevant to their business and industry.
Threat Detection and Response
Ensuring the security of cloud servers requires a proactive approach to threat detection and response. Cloud providers offer a range of tools and services to assist in this process.
Security monitoring tools play a crucial role in detecting potential threats by continuously analyzing system logs, network traffic, and other security-related data. These tools can identify suspicious activity, such as unauthorized access attempts, malware infections, or data breaches, and alert administrators to potential risks.
Incident Response Plans
In the event of a security incident, it is essential to have a well-defined incident response plan in place. This plan should Artikel the steps to be taken to contain the threat, mitigate its impact, and restore normal operations as quickly as possible.
The plan should include roles and responsibilities for key personnel, communication channels, and procedures for coordinating with external stakeholders, such as law enforcement or security vendors.
Cloud Security Best Practices: Cloud Diagram Server Security
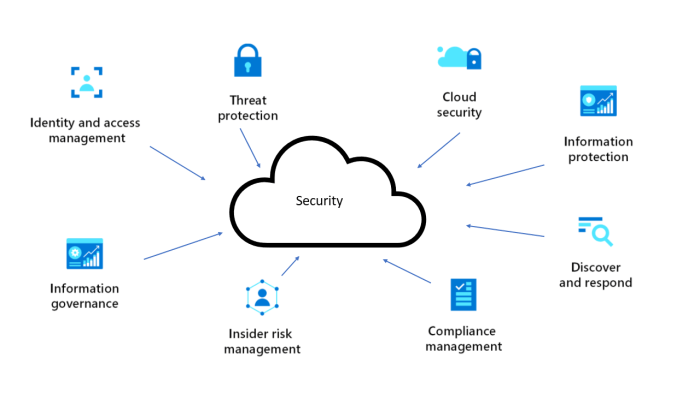
To ensure the security of cloud servers, it’s essential to adhere to a set of best practices. These practices cover various aspects of server management, including patch management, access control, and disaster recovery.
Patch Management
Regularly updating software and firmware patches is crucial for addressing security vulnerabilities. Cloud providers typically offer automated patch management services, making it easier to keep systems up-to-date.
Access Control
Implement strict access controls to prevent unauthorized access to cloud servers. This includes using strong passwords, enabling multi-factor authentication, and limiting access to only authorized personnel.
Disaster Recovery
Create a comprehensive disaster recovery plan to ensure business continuity in the event of a server outage. This plan should include regular backups, testing of recovery procedures, and coordination with cloud providers for support.
End of Discussion
In conclusion, cloud diagram server security is a multifaceted discipline that requires a comprehensive approach. By adhering to best practices, understanding cloud architectures, complying with security standards, and implementing effective threat detection and response mechanisms, organizations can safeguard their cloud environments and mitigate security risks.
This guide serves as a valuable resource for IT professionals, cloud architects, and business leaders seeking to enhance the security posture of their cloud-based systems.