Cloud Diagram Server Architecture: A Comprehensive Guide
Delve into the realm of Cloud diagram server architecture, where innovation and efficiency converge. This comprehensive guide unveils the intricate components, services, and security measures that underpin this transformative technology.
As businesses embrace the cloud, understanding server architecture becomes paramount. This guide provides a roadmap for navigating the complexities of cloud computing, empowering you to harness its full potential.
Server Architecture Overview
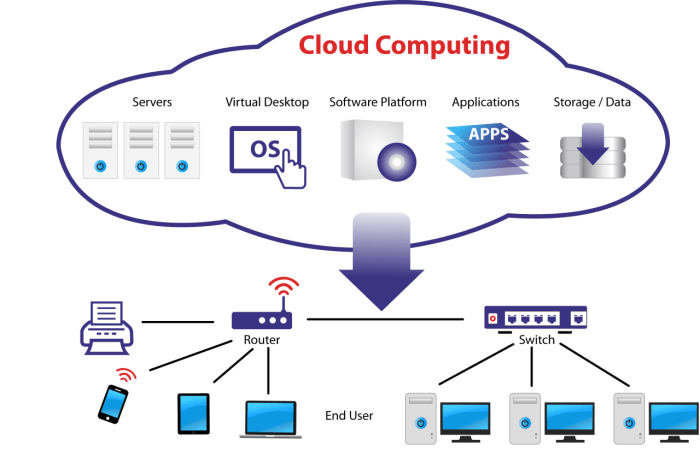
Cloud server architecture is a framework that Artikels the design and organization of servers within a cloud computing environment. It defines the components, their relationships, and the communication protocols used to build and manage cloud-based systems.
Cloud server architectures can vary in complexity, ranging from single-tier to multi-tier architectures. Single-tier architectures are the simplest, consisting of a single server that handles all aspects of the application, including data storage, processing, and presentation.
Multi-tier architectures, on the other hand, distribute the workload across multiple servers, each dedicated to a specific task. For example, a three-tier architecture might have a web server for handling client requests, an application server for processing business logic, and a database server for data storage.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Cloud Server Architectures
- Single-tier architectures are simple to implement and manage, but they can be less scalable and less fault-tolerant than multi-tier architectures.
- Multi-tier architectures are more scalable and fault-tolerant than single-tier architectures, but they can be more complex to implement and manage.
Cloud Services and their Integration
Cloud services offer a range of capabilities that can be integrated into a cloud server architecture to enhance its functionality and scalability. These services fall into three main categories:
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)provides fundamental computing resources such as servers, storage, and networking, allowing users to build and manage their own virtual infrastructure.
- Platform as a Service (PaaS)offers a platform for developing, deploying, and managing applications, eliminating the need for users to manage the underlying infrastructure.
- Software as a Service (SaaS)provides fully managed software applications that can be accessed over the internet, reducing the burden of software maintenance and updates.
Integrating cloud services into a server architecture brings several benefits. It enables businesses to:
- Reduce infrastructure costs:By leveraging cloud services, businesses can avoid the upfront capital expenses of purchasing and maintaining their own hardware.
- Increase scalability:Cloud services allow businesses to scale their infrastructure up or down as needed, providing greater flexibility and agility.
- Enhance reliability:Cloud providers typically offer high levels of uptime and redundancy, ensuring the availability of critical services.
However, integrating cloud services also poses some challenges:
- Vendor lock-in:Businesses may become dependent on a specific cloud provider, limiting their ability to switch providers in the future.
- Security concerns:Businesses need to carefully consider the security implications of storing and processing sensitive data in the cloud.
- Performance issues:Network latency and bandwidth limitations can impact the performance of cloud-based applications.
Despite these challenges, the benefits of integrating cloud services into a server architecture often outweigh the risks. By carefully considering the factors discussed above, businesses can leverage cloud services to improve their IT infrastructure and gain a competitive advantage.
Security Considerations in Cloud Server Architecture
Cloud server architectures present unique security challenges that must be addressed to ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of data and applications. Security risks can arise from various sources, including unauthorized access, data breaches, malware attacks, and denial-of-service (DoS) attacks.
To mitigate these risks, it is crucial to implement best practices for securing cloud servers. These practices include encryption of data at rest and in transit, robust access control mechanisms, and regular security audits.
Encryption
Encryption is essential for protecting data stored in the cloud from unauthorized access. Encryption algorithms, such as AES-256, can be used to encrypt data before it is uploaded to the cloud. This ensures that even if data is intercepted, it cannot be decrypted without the encryption key.
Access Control
Access control mechanisms restrict who can access cloud servers and the resources they contain. Role-based access control (RBAC) is a common approach that assigns different levels of access to users based on their roles within the organization. Additionally, multi-factor authentication (MFA) can be used to add an extra layer of security by requiring users to provide multiple forms of identification before accessing the cloud server.
Firewalls and Intrusion Detection Systems
Firewalls and intrusion detection systems (IDS) are essential components of cloud security. Firewalls block unauthorized access to the cloud server by filtering incoming and outgoing traffic based on predefined rules. IDS monitor network traffic for suspicious activity and can alert administrators to potential security threats.
Monitoring and Management of Cloud Servers: Cloud Diagram Server Architecture
In the dynamic realm of cloud computing, monitoring and managing cloud servers is paramount to ensure optimal performance, cost efficiency, and security. These servers, often distributed across multiple data centers, demand constant surveillance and proactive management to maintain their reliability and availability.
Monitoring Tools and Techniques
A plethora of monitoring tools and techniques are available to track key metrics of cloud servers. These tools provide real-time insights into resource utilization, performance, and availability. Common metrics include CPU usage, memory consumption, network traffic, and disk space. Advanced monitoring solutions also offer predictive analytics, anomaly detection, and automated alerting to proactively identify potential issues.
Best Practices for Managing Cloud Servers, Cloud diagram server architecture
Effective management of cloud servers requires a combination of best practices, including:
- Performance Optimization:Regularly monitor and analyze server performance to identify bottlenecks and optimize resource allocation. Consider using auto-scaling mechanisms to adjust capacity based on demand.
- Cost Control:Track cloud usage and costs to identify areas for optimization. Utilize cost-saving features such as spot instances and reserved instances to reduce expenses.
- Security Management:Implement robust security measures, including access control, intrusion detection, and vulnerability management. Regularly update security patches and conduct security audits to maintain a strong security posture.
- Disaster Recovery Planning:Develop and implement a comprehensive disaster recovery plan to ensure business continuity in the event of outages or disruptions. Consider using cloud-based disaster recovery services for enhanced resilience.
Future Trends in Cloud Server Architecture
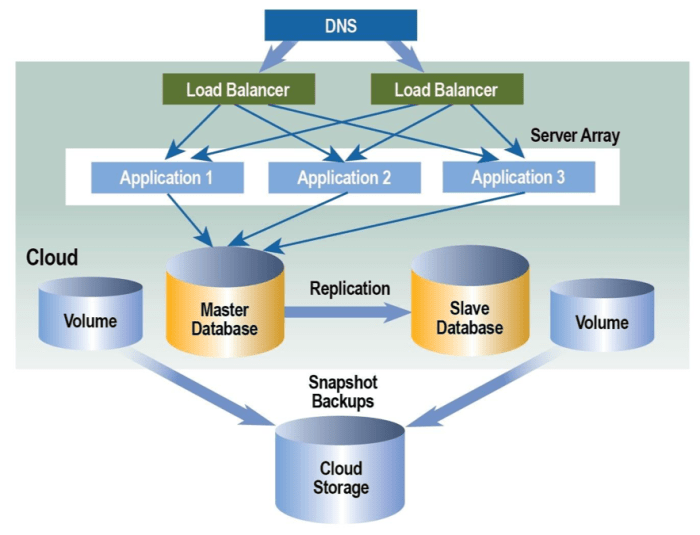
The future of cloud server architecture is shaped by emerging trends that will transform the way businesses leverage cloud computing. These trends include:
- Serverless Computing:A model where developers can build and deploy applications without managing servers or infrastructure, allowing for greater agility and cost optimization.
- Edge Computing:Processing and storing data closer to end-users, reducing latency and improving performance for applications that require real-time data access.
- Hybrid Cloud:Combining public cloud services with private cloud or on-premises infrastructure, providing flexibility and customization while maintaining control over sensitive data.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML):Integrating AI and ML into cloud server architecture to automate tasks, optimize performance, and provide predictive insights.
- Quantum Computing:Harnessing the power of quantum computers to solve complex problems and accelerate scientific discoveries.
These trends present both challenges and opportunities for businesses:
Challenges
- Managing complexity and security across diverse cloud environments.
- Adapting existing applications and infrastructure to leverage new cloud technologies.
- Ensuring data privacy and compliance in hybrid cloud environments.
Opportunities
- Increased agility and scalability to meet changing business needs.
- Reduced costs and improved efficiency through optimized resource utilization.
- Enhanced innovation and competitiveness by leveraging cutting-edge cloud technologies.
By embracing these trends and addressing the associated challenges, businesses can unlock the full potential of cloud server architecture to drive innovation, improve operational efficiency, and gain a competitive edge in the digital age.
Closing Notes
Cloud diagram server architecture stands as a testament to the ever-evolving landscape of technology. Its adaptability, scalability, and security make it an indispensable tool for businesses seeking to thrive in the digital age.
By embracing the insights presented in this guide, you gain the knowledge and confidence to design, implement, and manage cloud server architectures that drive innovation and empower your organization to reach new heights.