Cloud Diagram Server Deployment: An Architectural Guide
Embark on a journey into the realm of Cloud diagram server deployment, where we unravel the intricacies of cloud computing, unlocking its potential for businesses seeking scalability, security, and cost optimization.
From deciphering server deployment architecture to mastering cloud security and performance optimization techniques, this comprehensive guide will equip you with the knowledge and strategies to harness the power of the cloud.
Server Deployment Architecture
Cloud server deployment involves distributing servers across multiple physical locations to enhance accessibility, reliability, and scalability. This architecture provides a robust and flexible infrastructure for businesses and organizations.
The architecture consists of several key components, including:
- Servers:The physical or virtual machines that host applications and data.
- Network:The infrastructure that connects the servers and provides communication channels.
- Load balancers:Devices that distribute incoming traffic across multiple servers, ensuring optimal performance.
- Firewalls:Security measures that protect the network and servers from unauthorized access.
- Cloud management platform:A central interface for managing and monitoring the deployment.
Cloud server deployment offers several advantages, including:
- Scalability:The ability to easily add or remove servers as needed to meet changing demands.
- Reliability:Redundancy and failover mechanisms ensure high availability and minimize downtime.
- Cost-effectiveness:Pay-as-you-go pricing models allow businesses to optimize their infrastructure costs.
- Flexibility:The ability to deploy servers in different locations and configurations to meet specific requirements.
However, there are also some disadvantages to consider:
- Security:Cloud deployments require robust security measures to protect data and applications.
- Complexity:Managing a cloud deployment can be complex, especially for large-scale deployments.
- Vendor lock-in:Some cloud providers offer proprietary technologies that can limit flexibility and increase costs.
When choosing a deployment model, businesses should consider factors such as:
- Security requirements:Public clouds may not meet the security requirements of all organizations.
- Control and flexibility:Private clouds offer greater control and flexibility, but can be more expensive.
- Cost:Hybrid clouds can offer a balance between cost and flexibility.
Cloud Security Considerations: Cloud Diagram Server Deployment
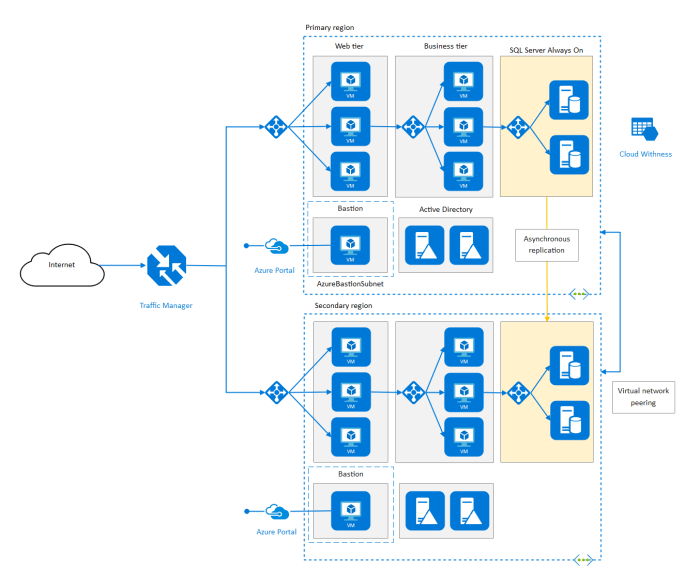
The transition to cloud-based server deployments introduces a unique set of security challenges that must be carefully addressed. Understanding these risks and implementing robust mitigation strategies is crucial for maintaining the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of data and systems in the cloud.
Cloud security risks stem from the shared nature of cloud infrastructure, the potential for unauthorized access, and the increased reliance on third-party providers. Effective cloud security involves implementing a comprehensive approach that addresses these risks at various levels.
Encryption
Encryption is a fundamental security measure that protects data both at rest and in transit. Encrypting data at rest ensures that it remains inaccessible to unauthorized parties, even if the physical storage devices are compromised. Encrypting data in transit protects against eavesdropping and man-in-the-middle attacks.
- Encrypt data using industry-standard algorithms like AES-256.
- Implement encryption at both the file system and database levels.
- Use encryption keys that are securely managed and regularly rotated.
Access Control
Access control mechanisms ensure that only authorized individuals can access cloud resources. Implementing granular access controls allows administrators to define who can access what data and services, and under what conditions.
- Use role-based access control (RBAC) to assign permissions based on user roles.
- Implement multi-factor authentication (MFA) to add an extra layer of security to user logins.
- Monitor and audit access logs to detect suspicious activity.
Data Backup
Regular data backups are crucial for protecting against data loss due to hardware failures, software errors, or malicious attacks. Cloud providers typically offer backup services, but it’s important to implement a comprehensive backup strategy that includes both on-premises and cloud-based backups.
- Create regular backups of all critical data and store them in a separate location.
- Test backups regularly to ensure they can be restored successfully.
- Implement automated backup processes to minimize the risk of human error.
Compliance and Standards
Cloud security should also adhere to relevant compliance requirements and industry standards. These regulations and standards provide guidelines for implementing secure cloud environments and protecting sensitive data.
- Obtain certifications such as ISO 27001 or SOC 2 to demonstrate compliance with industry standards.
- Follow best practices Artikeld by regulatory bodies like HIPAA or GDPR.
- Work with cloud providers that offer compliance-ready services.
Performance Optimization Techniques
Optimizing cloud server performance is crucial for ensuring smooth operations and user satisfaction. By implementing effective techniques, businesses can maximize the efficiency and responsiveness of their cloud-based infrastructure.Resource allocation plays a significant role in performance optimization. Proper sizing of virtual machines (VMs) and allocation of resources such as CPU, memory, and storage can prevent bottlenecks and ensure optimal performance.Load
balancing distributes incoming traffic across multiple servers, preventing any single server from becoming overwhelmed. This technique enhances scalability and ensures consistent performance under high load conditions.Caching mechanisms can significantly improve server performance by storing frequently accessed data in memory. By reducing the need to retrieve data from slower storage devices, caching accelerates data access and improves overall responsiveness.Monitoring
and troubleshooting tools are essential for identifying and resolving performance issues. Regular monitoring allows businesses to proactively identify potential problems and take corrective actions before they impact user experience. Troubleshooting tools provide insights into server performance metrics, helping administrators pinpoint the root cause of issues and implement effective solutions.
Cost Management Strategies
Managing cloud server deployment costs is crucial for optimizing resource utilization and minimizing expenses. Understanding pricing models and implementing effective cost-saving strategies is essential for efficient cloud operations.
Pricing Models
- Pay-as-you-go (PAYG):Billed based on actual resource usage, providing flexibility and scalability.
- Reserved Instances (RIs):Discounted pricing for committing to specific resources for a fixed period, offering significant cost savings for predictable workloads.
- Spot Instances:Utilize excess capacity at deeply discounted rates, ideal for non-critical or interruptible workloads.
Optimization Strategies
Optimizing cloud costs involves rightsizing resources to match actual needs and leveraging cost-effective options.
Rightsizing Resources
- Monitor resource utilization to identify underutilized or overprovisioned resources.
- Scale up or down resources based on demand patterns to avoid overspending or underutilization.
Spot Instances
- Use spot instances for workloads that can tolerate interruptions.
- Set appropriate bid prices to secure spot instances at competitive rates.
Tracking and Analysis
Regularly tracking and analyzing cloud usage and costs is crucial for effective cost management.
Tools and Techniques
- Cloud cost management tools provide detailed insights into resource consumption and expenses.
- Cloud providers offer dashboards and reports for monitoring usage patterns and identifying cost anomalies.
- Regularly review cost reports and implement cost-saving measures as needed.
Scalability and Availability Options
Ensuring scalability and availability is crucial for cloud server deployments to handle fluctuating workloads and maintain service continuity. Various options are available, each with its advantages and disadvantages.
Auto-Scaling, Cloud diagram server deployment
Auto-scaling dynamically adjusts the number of servers based on real-time demand. It helps optimize resource utilization, reducing costs during low traffic periods and ensuring sufficient capacity during peak times. Auto-scaling can be configured based on metrics like CPU utilization, memory usage, or custom metrics.
Load Balancing
Load balancing distributes incoming requests across multiple servers, improving performance and availability. It ensures that no single server becomes overloaded, preventing service disruptions. Load balancers can be hardware-based or software-based, with features like session persistence and health checks.
Failover Mechanisms
Failover mechanisms provide redundancy and ensure service availability in case of server failures. They involve creating redundant instances or setting up backup servers that can take over in the event of a primary server outage. Common failover mechanisms include active-passive failover and active-active failover.
Choosing the Appropriate Solution
The choice of scalability and availability solution depends on the specific application requirements. Factors to consider include:
- Workload patterns and traffic variability
- Service level agreements (SLAs) for availability and performance
- Cost considerations and budget constraints
- Complexity and management overhead of the solution
A combination of these options may be necessary to achieve the desired level of scalability and availability.
Closing Notes
As we conclude our exploration of Cloud diagram server deployment, remember that the cloud holds immense possibilities for businesses seeking to transform their IT infrastructure. By embracing the principles Artikeld in this guide, you can unlock the full potential of cloud computing, empowering your organization with agility, resilience, and cost-effectiveness.