Cloud vs Starlink: Unraveling the Optimal Internet Solution
In the realm of internet connectivity, Cloud vs Starlink: Choosing the Best Internet Solution emerges as a pivotal discourse. As we delve into the depths of this topic, we will explore the intricacies of these two services, unraveling their strengths, limitations, and suitability for various needs.
The second paragraph will provide an overview of the key aspects to consider when comparing Cloud and Starlink, including speed, coverage, cost, reliability, and security. We will delve into the nuances of each aspect, providing a comprehensive analysis to guide readers in making informed decisions.
Speed and Latency
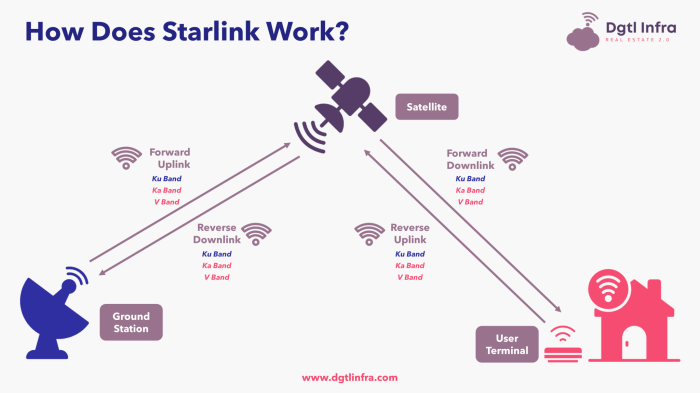
Cloud and Starlink offer varying speeds and latency, impacting the user experience for online activities. Understanding these differences is crucial for choosing the best solution.
Starlink boasts higher download speeds, ranging from 50 to 500 Mbps, while Cloud typically provides speeds between 10 to 100 Mbps. However, Starlink’s upload speeds are slower, ranging from 10 to 50 Mbps, compared to Cloud’s 10 to 500 Mbps.
Latency
Latency, the time taken for data to travel between devices, is crucial for real-time applications like online gaming and video conferencing. Starlink’s latency is higher, ranging from 20 to 100 milliseconds, while Cloud offers lower latency, typically between 10 to 50 milliseconds.
Lower latency is essential for seamless gaming, video calls, and other applications where quick response times are critical.
As you weigh your options between Cloud and Starlink for the best internet solution, it’s worth considering the advancements on the horizon. Starlink’s ongoing technological evolution, as detailed in Satellite Internet Technology Evolution in Starlink 2024 , promises significant improvements in speed, coverage, and latency.
These enhancements could further strengthen Starlink’s position as a competitive choice for high-speed internet access. By staying informed about the latest developments, you can make an informed decision that aligns with your evolving connectivity needs.
Coverage and Availability
Cloud and Starlink offer varying coverage and availability, catering to different geographic regions and population densities.
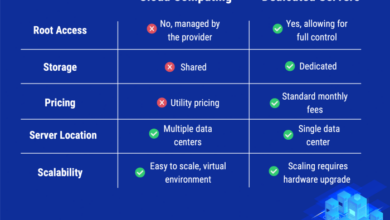
Cloud services typically rely on terrestrial infrastructure, such as fiber optic cables and cell towers, which limits their reach to urban and suburban areas. Starlink, on the other hand, utilizes a constellation of satellites in low Earth orbit, providing coverage to a wider range of locations, including rural and remote areas.
Cloud and Starlink offer distinct advantages, but for those seeking an affordable and accessible internet solution, Starlink’s upcoming 2024 launch presents a promising option. Starlink’s satellite-based network aims to provide high-speed internet to remote and underserved areas, potentially bridging the digital divide.
Returning to our comparison, Cloud services remain a robust choice for urban environments, but Starlink’s affordability and expanding coverage make it a compelling contender in the ongoing Cloud vs Starlink debate.
Coverage Areas
- Cloud: Concentrated in densely populated areas, with limited availability in rural regions.
- Starlink: Global coverage, including remote and underserved areas with limited or no existing internet infrastructure.
Availability in Rural and Remote Locations
Starlink has a clear advantage in rural and remote locations where traditional broadband infrastructure is lacking. Its satellite network allows for internet connectivity in areas previously unreachable by terrestrial services.
Cloud services, on the other hand, may not be available or offer limited connectivity options in such areas, leaving residents with fewer internet access choices.
Potential Limitations and Restrictions, Cloud vs Starlink: Choosing the Best Internet Solution
While Starlink offers extensive coverage, it may face challenges during adverse weather conditions, such as heavy rain or snow, which can disrupt satellite signals.
Cloud services, on the other hand, are generally less susceptible to weather-related interruptions but may have data usage limits or other restrictions imposed by the provider.
Cost and Value

When selecting an internet solution, the cost and value proposition are crucial considerations. Let’s delve into the pricing and features of Cloud and Starlink to determine which service offers the best value for money.
Monthly Subscription Fees
- Cloud offers flexible subscription plans starting at $59 per month, providing various speed options tailored to different needs.
- Starlink has a fixed monthly fee of $110, regardless of speed or data usage, which may be more cost-effective for high-bandwidth users.
Installation Costs
- Cloud typically requires minimal installation costs, ranging from $0 to $100, depending on the installation complexity.
- Starlink, on the other hand, has a significant one-time installation cost of $599, which includes the Starlink dish and necessary hardware.
Additional Expenses
- Cloud may incur additional charges for equipment rental or upgrades, depending on the chosen plan and usage.
- Starlink has no additional equipment rental fees, but users may need to purchase a Wi-Fi router for wireless connectivity, which typically costs around $50-$150.
Cost-to-Benefit Ratio
Evaluating the cost-to-benefit ratio helps determine the overall value of each service. Cloud offers lower monthly fees and installation costs, making it a more budget-friendly option for moderate bandwidth users. Starlink’s higher upfront cost and monthly fee may be justified for users requiring high-speed, low-latency internet in remote areas where traditional broadband is unavailable.
Reliability and Stability
When it comes to internet connectivity, reliability and stability are crucial factors to consider. Cloud and Starlink offer different approaches to internet delivery, and their reliability and stability profiles vary accordingly.
Whether you’re considering Cloud or Starlink for your internet solution, it’s crucial to stay informed about the latest advancements in satellite technology. For an in-depth analysis of Starlink’s future, check out the comprehensive article: Future of Satellite Internet with Starlink 2024 . This article explores the groundbreaking developments expected with Starlink’s upcoming upgrades, providing valuable insights for making an informed decision between Cloud and Starlink for your internet needs.
Uptime Rates and Outages
Uptime rate refers to the percentage of time that an internet connection is available and functioning properly. Cloud-based internet services typically have high uptime rates, as they are hosted on redundant servers in multiple data centers. This means that if one server experiences an outage, the service can quickly failover to another server, minimizing downtime for users.
Starlink, on the other hand, relies on a constellation of satellites in low Earth orbit. While this provides coverage to remote areas, it can be more susceptible to outages caused by factors such as satellite failures, weather conditions, and solar flares.
However, Starlink has implemented measures to mitigate these risks, such as using multiple satellites to provide redundancy and incorporating advanced algorithms to optimize network performance.
Impact of Weather Conditions
Weather conditions can significantly impact the reliability of internet connections. Cloud-based services are generally not affected by weather, as they are not reliant on line-of-sight connections. Starlink, however, can be affected by heavy rain, snow, and high winds, which can interfere with the satellite signals.
Starlink has taken steps to address this issue by using advanced satellite technology that can withstand harsh weather conditions. Additionally, Starlink is continuously working to improve its network resilience and minimize the impact of weather-related outages.
Security and Privacy
Cloud and Starlink prioritize user data protection and privacy through various security measures and privacy policies.
Both services employ encryption technologies to safeguard data during transmission and storage, ensuring confidentiality. Additionally, they implement multi-factor authentication for account access, adding an extra layer of security against unauthorized login attempts.
Data Storage and Management
- Cloud: Data is stored in secure data centers with restricted physical access and advanced intrusion detection systems.
- Starlink: Data is encrypted and distributed across a network of ground stations and satellites, providing redundancy and protection against data loss.
Privacy Policies
Cloud and Starlink adhere to industry privacy standards, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), ensuring compliance with data protection regulations.
However, it’s important to note that no internet service is entirely immune to potential vulnerabilities or risks.
Potential Vulnerabilities
- Cloud: Cloud storage can be susceptible to cyberattacks, including data breaches and ransomware.
- Starlink: The satellite network may be vulnerable to signal interception or jamming, potentially compromising data privacy.
Ultimately, the best choice for security and privacy depends on the specific needs and risk tolerance of individual users.
Closing Summary: Cloud Vs Starlink: Choosing The Best Internet Solution

In conclusion, the choice between Cloud and Starlink hinges on individual requirements and circumstances. By carefully weighing the factors discussed in this article, readers can confidently select the internet solution that aligns seamlessly with their needs, ensuring an optimal online experience.
Detailed FAQs
Which service offers faster speeds?
Starlink generally provides faster download speeds, while Cloud offers more consistent upload speeds.
Is Starlink available in remote areas?
Yes, Starlink’s satellite network provides coverage in many remote locations where traditional internet services are unavailable.
Is Cloud more secure than Starlink?
Both Cloud and Starlink implement robust security measures, but Cloud’s infrastructure and regulatory compliance may offer additional layers of protection.