Cloud vs Starlink: Shaping the Future of Connectivity and Innovation
Cloud vs Starlink: Future Trends and Technological Advancements sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail and brimming with originality from the outset. This captivating exploration delves into the fundamental differences between these two groundbreaking platforms, their impact on the technological landscape, and their potential to revolutionize the way we connect and innovate in the years to come.
As we embark on this journey, we will uncover the key enabling technologies that drive Cloud and Starlink, unravel their cost structures and accessibility challenges, and explore the myriad of use cases and applications that are shaping their future. We will also examine the security measures and reliability guarantees that underpin these platforms, ensuring that our digital ventures are protected and uninterrupted.
Technological Advancements

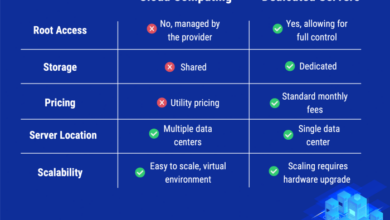
Cloud computing and Starlink represent distinct approaches to delivering computing and connectivity services. Cloud computing leverages vast networks of remote servers to provide scalable, on-demand access to computing resources and applications. Starlink, on the other hand, utilizes a constellation of low-earth orbit (LEO) satellites to deliver high-speed, low-latency broadband internet access to remote and underserved areas.
Key Enabling Technologies
Cloud computing relies on virtualization and distributed computing technologies to create a pool of shared computing resources. These resources are dynamically allocated to users based on their demand, enabling efficient utilization and cost optimization. Starlink, in contrast, leverages satellite technology to establish a direct connection between users and the internet backbone, bypassing traditional terrestrial infrastructure.
Future Technological Advancements
Both cloud computing and Starlink are poised for significant technological advancements in the coming years. Cloud computing is expected to embrace edge computing, artificial intelligence (AI), and quantum computing, enabling more distributed, intelligent, and secure computing capabilities. Starlink, meanwhile, is exploring advancements in satellite technology, such as higher bandwidth and lower latency, to further enhance its connectivity services.
Cost and Accessibility: Cloud Vs Starlink: Future Trends And Technological Advancements
Cloud and Starlink present distinct cost structures and pricing models, with implications for accessibility. Factors such as geographical coverage and latency further influence accessibility.
As the technological landscape continues to evolve, the ongoing debate between Cloud and Starlink remains at the forefront of discussions surrounding future trends and advancements. Starlink’s ambitious plans for 2024 promise significant improvements in internet speed and latency, as outlined in Starlink 2024 Internet Speed and Latency Improvements . These enhancements will undoubtedly impact the ongoing discourse on Cloud vs Starlink, shaping the future of connectivity and pushing the boundaries of technological innovation.
Cloud services typically charge based on usage, with tiered pricing models that vary depending on the specific services and resources consumed. This pay-as-you-go approach can be cost-effective for businesses that experience fluctuating or unpredictable usage patterns.
Cost Structure and Pricing
- Cloud: Pay-as-you-go model based on usage, with tiered pricing for different services and resources.
- Starlink: Subscription-based model with fixed monthly fees for internet access, regardless of usage.
Geographical Coverage and Latency
Geographical coverage is a key factor affecting accessibility. Cloud services are widely available globally, while Starlink’s coverage is currently limited to certain regions. Latency, which refers to the delay in data transmission, can also impact accessibility, especially for real-time applications.
In the realm of future trends, the battle between Cloud and Starlink is a topic that continues to ignite discussions. As we eagerly anticipate the technological advancements that will shape our connectivity landscape, let’s not overlook the pivotal role of Starlink 2024 in revolutionizing global connectivity.
Starlink 2024 promises to bring high-speed, low-latency internet access to remote and underserved areas, blurring the boundaries of digital divides. However, as we witness the ongoing evolution of Cloud computing and its potential to enhance connectivity, the interplay between these technologies remains an intriguing area to watch, promising to shape the future of our connected world.
- Cloud: Wide geographical coverage with low latency in major population centers.
- Starlink: Expanding coverage but currently limited to specific regions; latency may vary depending on location.
Potential for Cost Reductions and Improved Accessibility
Cost reductions and improved accessibility are likely in the future for both Cloud and Starlink. Cloud providers are exploring cost optimization strategies, while Starlink is expanding its coverage and working to reduce latency. Advances in satellite technology and the development of new low-earth orbit (LEO) constellations could further enhance accessibility.
- Cloud: Cost optimization strategies and advancements in virtualization technologies.
- Starlink: Expanding coverage, reducing latency, and exploring LEO constellations.
Use Cases and Applications
Cloud computing and Starlink satellite internet have diverse use cases and applications across various industries and scenarios. Each platform offers unique advantages and limitations, catering to specific needs.
Business Applications
Cloud computing empowers businesses with scalable and cost-effective solutions for data storage, processing, and application hosting. It facilitates remote work, collaboration, and access to enterprise-grade applications, enhancing productivity and efficiency.Starlink, with its low-latency and high-speed internet connectivity, enables remote offices and rural areas to access reliable internet services.
It supports video conferencing, cloud-based software, and real-time data transfer, facilitating business continuity and expansion into underserved regions.
Healthcare
Cloud computing provides secure and accessible storage for patient records, medical imaging, and research data. It enables remote patient monitoring, telemedicine, and data analytics for improved healthcare delivery.Starlink’s reliable internet connectivity facilitates telemedicine consultations, remote patient monitoring, and access to healthcare information in remote and underserved communities, addressing healthcare disparities.
Education
Cloud computing offers virtual learning platforms, online collaboration tools, and access to educational resources. It enables remote learning, personalized education, and anytime, anywhere access to knowledge.Starlink provides high-speed internet access to schools and educational institutions in rural and remote areas, bridging the digital divide and enhancing educational opportunities.
Emerging Use Cases, Cloud vs Starlink: Future Trends and Technological Advancements
The convergence of cloud computing and Starlink satellite internet opens up new possibilities and emerging use cases. These include:
Autonomous vehicles
Cloud computing provides real-time data processing and storage for autonomous vehicle navigation, while Starlink ensures reliable connectivity for communication and software updates.
Smart cities
Cloud computing supports data analytics and IoT integration for smart city management, while Starlink enables ubiquitous internet access for smart infrastructure and citizen engagement.
Remote work and digital nomadism
Cloud computing and Starlink empower remote workers and digital nomads to access enterprise-grade applications and reliable internet connectivity from anywhere.
Security and Reliability

Security and reliability are crucial aspects to consider when evaluating cloud and satellite internet services. Both platforms employ robust security measures and protocols to safeguard user data and ensure network stability.
Cloud and Starlink represent contrasting yet complementary approaches to internet connectivity. While Cloud offers scalability and reliability, Starlink focuses on reaching remote and underserved areas. This dichotomy is exemplified by the upcoming Starlink 2024 project, which aims to bridge the digital divide . As Starlink expands its reach, it challenges the dominance of Cloud-based services, fostering a dynamic interplay between these technologies that will shape the future of internet access.
Cloud platforms utilize encryption technologies, access controls, and regular security audits to protect data stored and processed on their servers. Starlink, on the other hand, employs advanced encryption algorithms and authentication protocols to secure data transmissions and prevent unauthorized access to its network.
Reliability and Uptime Guarantees
Cloud platforms typically offer high levels of reliability with uptime guarantees ranging from 99.9% to 99.99%. This ensures minimal service interruptions and consistent performance for users.
Starlink, while still in its early stages of deployment, aims to provide comparable reliability with uptime targets of 99%. However, it is important to note that satellite internet is subject to factors such as weather conditions and geographic location, which can potentially impact service availability.
Potential Risks and Challenges
Despite the security measures in place, both cloud and Starlink platforms face potential risks and challenges.
- Cloud:Cloud platforms can be vulnerable to cyberattacks, data breaches, and service outages due to hardware failures or software glitches.
- Starlink:Satellite internet is susceptible to signal interference from weather conditions, obstructions, and geographic limitations, which can affect service quality and availability.
It is essential for users to carefully consider the security and reliability requirements of their applications and choose the platform that best meets their needs.
Market Trends and Competition
The Cloud and Starlink markets are rapidly evolving, with new technologies and players emerging constantly. Cloud computing is becoming increasingly popular as businesses realize the benefits of scalability, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness. Starlink, on the other hand, is a new player in the satellite internet market, offering high-speed, low-latency internet access to remote areas.
Key Players and Competitive Strategies
The key players in the Cloud market include Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP). These companies are competing on price, features, and customer service. AWS is the current market leader, but Azure and GCP are gaining market share.
In the Starlink market, SpaceX is the dominant player. The company has a significant first-mover advantage and is rapidly expanding its network.
Potential for Consolidation or Partnerships
There is potential for consolidation or partnerships in both the Cloud and Starlink markets. In the Cloud market, smaller players may be acquired by larger players or may form partnerships to compete with the larger players. In the Starlink market, SpaceX may partner with other companies to expand its reach or to offer additional services.
Conclusive Thoughts

In the concluding chapter of our exploration, we will delve into the competitive dynamics that shape the Cloud and Starlink markets, identifying key players and their strategies. We will also speculate on the potential for consolidation or partnerships, and explore the broader implications for the future of connectivity and innovation.
As we reach the end of our journey, we will have gained a comprehensive understanding of these two transformative technologies and their profound impact on our digital world.
FAQ Overview
What are the key differences between Cloud and Starlink?
Cloud computing involves accessing computing resources over the internet, while Starlink provides internet access via a network of satellites.
Which platform is more cost-effective?
The cost of Cloud and Starlink services varies depending on factors such as usage, location, and bandwidth requirements.
What are the security implications of using Cloud and Starlink?
Both Cloud and Starlink employ robust security measures to protect user data and privacy.