Cloud vs Starlink: Exploring the Pros and Cons of Each Technology
Cloud vs Starlink: Pros and Cons of Each Technology invites readers to embark on an informative journey, where we delve into the intricacies of two cutting-edge technologies, unraveling their strengths and limitations with a keen eye for detail.
From speed and latency to cost and security, we’ll navigate the complexities of these technologies, empowering you with the knowledge to make informed decisions about your connectivity needs.
Speed and Latency
Cloud and Starlink offer varying speeds and latency, affecting the user experience in different ways.
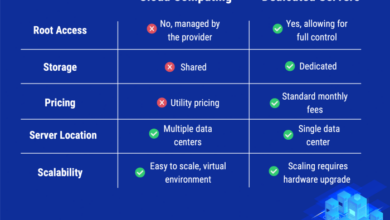
Cloud services typically provide faster download and upload speeds than Starlink. This is because Cloud servers are located closer to end-users, reducing the distance data must travel and resulting in lower latency.
Latency
Latency refers to the time it takes for data to travel between two points. Lower latency is crucial for real-time applications like gaming and video conferencing, where even a slight delay can impact performance.
Cloud services generally have lower latency than Starlink due to their proximity to end-users. For example, a user in New York City connecting to a Cloud server in the same city would experience lower latency compared to connecting to a Starlink satellite located thousands of miles away.
Reliability and Availability

Cloud and Starlink technologies offer varying levels of reliability and availability, influenced by their respective infrastructure and deployment strategies.
Outage Potential and Downtime
Cloud services are susceptible to outages due to server failures, network disruptions, and software glitches. These outages can range from brief interruptions to extended periods of downtime, affecting service accessibility for users. In contrast, Starlink’s satellite-based architecture provides inherent resilience, reducing the likelihood of widespread outages.
However, localized outages can still occur due to factors such as satellite malfunctions or weather conditions.
While Cloud and Starlink offer distinct advantages and drawbacks, their potential to bridge the digital divide is equally significant. Starlink’s ambitious 2024 goal of expanding internet access, as outlined in Bridging the Digital Divide with Starlink 2024 , highlights the transformative power of satellite technology.
By complementing the capabilities of Cloud services, Starlink can empower remote and underserved communities with the connectivity they need to thrive in the digital age. As we navigate the pros and cons of both technologies, it’s crucial to consider their combined impact on bridging the digital divide and ensuring equitable access to the internet for all.
Geographic Coverage and Availability
Cloud services have a global reach, with data centers located in various regions worldwide. This ensures widespread availability and low latency for users in densely populated areas. However, access to cloud services can be limited in remote or underserved locations.
Starlink, on the other hand, aims to provide global coverage by deploying a constellation of satellites in low Earth orbit. This approach expands internet access to areas with limited or no terrestrial infrastructure, making it a viable option for rural and underserved communities.
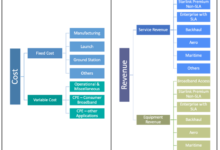
Cost and Value
When evaluating the cost and value of Cloud and Starlink, it’s important to consider both the upfront expenses and the ongoing subscription fees. Additionally, the potential return on investment (ROI) should be taken into account, as this can vary depending on the specific use case.
Subscription Fees, Cloud vs Starlink: Pros and Cons of Each Technology
- Cloud services typically offer a pay-as-you-go pricing model, where users are charged based on their usage. This can be advantageous for businesses that experience fluctuating bandwidth requirements.
- Starlink, on the other hand, offers a flat monthly subscription fee. This can provide businesses with a more predictable cost structure, but it may not be the most cost-effective option for businesses with low bandwidth usage.
Equipment Costs
- Cloud services do not require any specialized equipment, as all resources are accessed over the internet. This can save businesses a significant amount of money on hardware costs.
- Starlink requires users to purchase a satellite dish and modem, which can add to the overall cost of the service. However, Starlink’s equipment is designed to be easy to install and maintain, which can save businesses on IT support costs.
Additional Expenses
- Cloud services may require businesses to pay for additional features or services, such as data storage or backup. These costs can vary depending on the provider and the specific services required.
- Starlink does not have any additional expenses beyond the monthly subscription fee, making it a more predictable cost option for businesses.
Return on Investment
The ROI for Cloud and Starlink can vary depending on the specific use case. For businesses that require high bandwidth and low latency, Cloud services may offer a better ROI due to their superior performance. However, for businesses that require a more affordable and reliable option, Starlink may be a better choice.
Security and Privacy
Cloud and Starlink prioritize user security and privacy through various measures. These measures aim to protect user data, ensure confidentiality, and prevent unauthorized access.
Data Encryption
Both Cloud and Starlink implement robust data encryption mechanisms. Cloud uses industry-standard encryption algorithms to protect data at rest and in transit. Starlink employs end-to-end encryption, ensuring that data is encrypted from the user’s device to the destination server, protecting it from eavesdropping and unauthorized access.
The debate between Cloud and Starlink technologies has been ongoing, with each offering its own set of advantages and disadvantages. However, the recent announcement of Affordable Internet Access through Starlink 2024 has brought a new dimension to this discussion. With its promise of providing high-speed internet at a fraction of the cost, Starlink has the potential to revolutionize internet access, particularly in remote and underserved areas.
As the development of both Cloud and Starlink technologies continues, it will be interesting to see how they evolve and complement each other in shaping the future of internet connectivity.
Authentication and Authorization
Cloud and Starlink utilize multi-factor authentication and role-based access control to prevent unauthorized access. Multi-factor authentication requires users to provide multiple forms of identification, while role-based access control restricts user access to specific resources based on their designated roles.
While both Cloud and Starlink technologies offer distinct advantages and drawbacks, it’s worth considering the potential of Starlink 2024 for internet connectivity in remote areas. As discussed in the article ” Internet Connectivity in Remote Areas with Starlink 2024 “, Starlink’s satellite constellation aims to provide high-speed, low-latency internet access to underserved regions.
This development could significantly impact the availability and quality of internet connectivity for those living or working in remote locations, further shaping the landscape of Cloud vs Starlink technologies.
Compliance and Certifications
Cloud and Starlink adhere to industry-recognized security standards and certifications, such as ISO 27001 and SOC 2. These certifications demonstrate that their security practices meet stringent requirements, ensuring the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of user data.
Privacy Concerns
While Cloud and Starlink prioritize data privacy, some concerns have been raised. Cloud has been subject to scrutiny due to its close ties to governments and potential for data sharing. Starlink, on the other hand, has raised concerns about data collection and potential surveillance capabilities.
It’s important to note that both Cloud and Starlink have taken steps to address these concerns, implementing transparency measures and user-centric privacy policies. However, users should be aware of the potential privacy implications and take appropriate precautions to protect their data.
Specific Applications
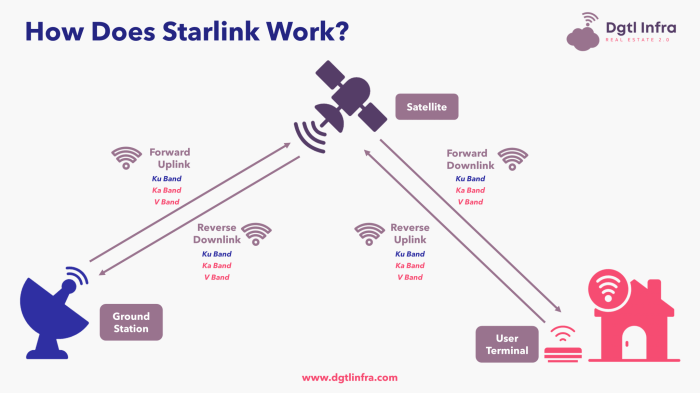
Cloud computing and Starlink satellite internet are two distinct technologies with unique strengths and weaknesses. Their ideal applications vary depending on the specific requirements of the user.
Cloud Computing
Cloud computing excels in applications that require high computing power, scalability, and accessibility from multiple locations. Examples include:
- Data processing and analysis
- Software development and testing
- Web hosting and content delivery
- Enterprise resource planning (ERP) and customer relationship management (CRM)
- Online collaboration and productivity tools
Starlink Satellite Internet
Starlink satellite internet is ideal for applications that require reliable, high-speed internet connectivity in remote or underserved areas. Examples include:
- Rural broadband internet access
- Maritime and aviation internet connectivity
- Emergency communications
- Disaster recovery
- Off-grid living and remote work
Last Point

As we conclude our exploration of Cloud vs Starlink, it’s evident that both technologies offer unique advantages and considerations. Whether your priority is lightning-fast speeds, reliable coverage, or cost-effectiveness, understanding the nuances of each technology will guide you toward the optimal choice for your specific requirements.
As the technological landscape continues to evolve, Cloud and Starlink will undoubtedly play pivotal roles in shaping our future connectivity. Stay tuned for further developments in this captivating realm of innovation.
Question Bank: Cloud Vs Starlink: Pros And Cons Of Each Technology
Which technology offers faster speeds: Cloud or Starlink?
Starlink generally provides faster download and upload speeds compared to Cloud, particularly in remote areas.
What are the latency differences between Cloud and Starlink?
Cloud typically has lower latency than Starlink, making it more suitable for real-time applications like gaming and video conferencing.
Is Starlink more reliable than Cloud?
Starlink offers more consistent connectivity, especially in areas with limited or unreliable terrestrial infrastructure. However, both technologies are susceptible to outages caused by factors such as weather and equipment failures.
Which technology is more cost-effective: Cloud or Starlink?
Cloud is generally more cost-effective than Starlink, especially for users with moderate bandwidth requirements. Starlink’s higher subscription fees and equipment costs may be justified for users in remote areas or with high bandwidth demands.