Cloud vs Starlink: Ushering in a Connectivity Revolution in 2024
Cloud vs Starlink: Revolutionizing Connectivity in 2024 – As the world hurtles towards the digital age, connectivity has become the lifeblood of modern society. In this realm, two titans emerge, poised to reshape the landscape: Cloud and Starlink. This article delves into the transformative potential of these technologies, exploring their features, applications, and the impact they will have on our lives in the years to come.
With the advent of Cloud and Starlink, the boundaries of connectivity are poised to expand exponentially, offering unprecedented opportunities for individuals, businesses, and entire industries. As we delve into the intricacies of these technologies, we will uncover the factors that differentiate them, their strengths and limitations, and the myriad ways in which they will revolutionize the way we connect and communicate.
Cloud and Starlink

The realm of internet connectivity is undergoing a transformative revolution, propelled by the advent of Cloud and Starlink technologies. Cloud computing, with its vast network of remote servers, has redefined data storage and processing, while Starlink, a constellation of low-Earth orbit (LEO) satellites, is redefining broadband internet access.
These technologies, distinct in their infrastructure and service offerings, are poised to reshape the digital landscape in 2024 and beyond.
Key Features and Comparison
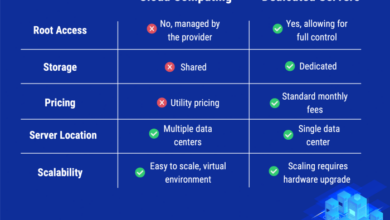
Cloud computing operates on a pay-as-you-go model, offering a scalable and cost-effective solution for businesses and individuals alike. Its distributed infrastructure enables access to computing resources, applications, and data from any internet-connected device. Starlink, on the other hand, utilizes a network of satellites to provide high-speed, low-latency internet connectivity to remote and underserved areas.
It aims to bridge the digital divide and bring reliable broadband access to regions with limited terrestrial infrastructure.
Cloud and Starlink are poised to revolutionize connectivity in 2024, offering unprecedented global access to the internet. Starlink’s ambitious Starlink 2024 Global Internet Access project aims to provide high-speed, low-latency internet to even the most remote areas, bridging the digital divide and empowering communities worldwide.
As these technologies continue to evolve, they will reshape the way we connect, communicate, and innovate, ushering in a new era of seamless connectivity for all.
Infrastructure and Service Offerings
Cloud computing relies on a network of interconnected data centers, housing servers that host applications, store data, and provide computing power. This infrastructure enables the delivery of a wide range of cloud services, including Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS).
Starlink, in contrast, operates a constellation of LEO satellites that orbit the Earth, providing coverage to a wide geographical area. These satellites are equipped with advanced communication systems, allowing for high-speed data transmission with minimal latency.
Performance and Reliability

Cloud and Starlink offer varying levels of performance and reliability, significantly impacting different use cases and industries. Key metrics to consider include latency, bandwidth, and uptime.
Latency
- Latency, the time delay in data transmission, is crucial for real-time applications like gaming, video conferencing, and remote surgery.
- Cloud services typically have lower latency due to their proximity to data centers, while Starlink’s satellite-based system introduces additional delay.
- For latency-sensitive applications, Cloud may provide a more consistent and reliable experience.
Bandwidth
- Bandwidth refers to the amount of data that can be transmitted over a network, affecting download and upload speeds.
- Starlink boasts higher potential bandwidth than Cloud, enabling faster data transfer for large files and streaming.
- However, factors like satellite coverage and congestion can impact Starlink’s bandwidth in certain areas.
Uptime
- Uptime measures the availability of a network service, indicating how often it is accessible and operational.
- Cloud services generally have high uptime rates due to their redundant infrastructure and multiple data centers.
li>Starlink’s uptime can be affected by weather conditions, satellite outages, and other factors related to its satellite network.
These factors collectively influence the suitability of Cloud and Starlink for various use cases. Cloud’s lower latency and consistent uptime make it ideal for latency-sensitive applications and mission-critical operations, while Starlink’s high bandwidth and global coverage excel in areas with limited terrestrial connectivity.
Applications and Use Cases: Cloud Vs Starlink: Revolutionizing Connectivity In 2024

Cloud and Starlink offer a wide range of applications and use cases, transforming industries and enabling new possibilities.Cloud computing provides scalable, on-demand access to computing resources, storage, and applications, while Starlink’s satellite constellation delivers high-speed, low-latency internet connectivity to remote areas.
Healthcare
Cloud and Starlink are revolutionizing healthcare by enabling remote patient monitoring, telemedicine, and data-driven medical research. Patients in remote areas can access specialist consultations and receive real-time medical advice. Cloud-based medical records improve patient care coordination and enhance clinical decision-making.
Education
Cloud and Starlink are transforming education by providing access to online learning platforms, virtual classrooms, and educational resources. Students in remote areas can participate in interactive lessons and collaborate with peers from different locations. Cloud-based learning management systems streamline educational administration and track student progress.
Remote Work
Cloud and Starlink are enabling remote work by providing secure access to corporate networks, applications, and data. Employees can work from anywhere with a stable internet connection, enhancing flexibility and productivity. Cloud-based collaboration tools facilitate seamless communication and document sharing.
Future Applications
The convergence of Cloud and Starlink holds immense potential for new and innovative applications. These include:
- Autonomous vehicles relying on cloud-based AI and Starlink connectivity for navigation and decision-making.
- Smart cities using cloud-based data analytics and Starlink connectivity to optimize traffic flow, energy consumption, and public safety.
- Immersive virtual reality and augmented reality experiences powered by cloud computing and Starlink’s high-speed internet.
Deployment and Accessibility
Cloud and Starlink’s deployment strategies and infrastructure requirements differ significantly. Cloud relies on existing terrestrial networks and data centers, while Starlink utilizes a constellation of low-earth orbit (LEO) satellites.
Cloud’s infrastructure is well-established and widely accessible, particularly in urban areas. However, it can face limitations in remote and underserved regions where physical infrastructure is limited.
Starlink’s Deployment
Starlink’s deployment involves launching and maintaining a vast network of LEO satellites. These satellites provide coverage over a wide area, including remote locations not served by traditional terrestrial networks.
Starlink’s satellite constellation requires specialized ground stations to communicate with the satellites and relay data to users. The company is actively expanding its ground station infrastructure to increase coverage and capacity.
Accessibility in Underserved Areas
Both Cloud and Starlink have the potential to expand connectivity to underserved areas. Cloud can leverage existing infrastructure and partnerships to provide cloud-based services in remote locations.
Starlink’s satellite-based technology offers a unique advantage in reaching remote areas with limited terrestrial infrastructure. It has the potential to bridge the digital divide and provide internet access to communities that have been historically underserved.
However, challenges remain in expanding connectivity to all underserved areas. Factors such as cost, regulatory hurdles, and terrain can affect the feasibility and accessibility of these technologies in certain regions.
Cost and Pricing Models
Cloud and Starlink adopt different pricing models, catering to the varying needs and usage patterns of their respective users. Understanding the cost structure and pricing factors is crucial for businesses and individuals to make informed decisions when choosing between these technologies.
As Cloud and Starlink gear up to redefine connectivity in 2024, let’s not overlook the remarkable strides being made in satellite internet technology, particularly in the realm of Starlink. Check out our in-depth analysis at Satellite Internet Technology Evolution in Starlink 2024 . These advancements will play a pivotal role in shaping the future of connectivity, complementing the revolutionary impact of Cloud and Starlink.
Cloud services typically employ a pay-as-you-go model, where users are charged based on their actual usage. This model offers flexibility and cost efficiency for organizations with fluctuating or unpredictable bandwidth requirements. Cloud providers generally charge based on factors such as the amount of data transferred, storage space utilized, and compute resources consumed.
Factors Influencing Pricing
- Bandwidth:Higher bandwidth tiers usually come with higher costs, as they require more network infrastructure and resources to deliver faster speeds.
- Usage:Cloud and Starlink services often charge based on the amount of data consumed. Heavy users can expect to pay more than those with moderate or low usage.
- Location:Geographical factors can also influence pricing, with certain regions having higher costs due to infrastructure limitations or regulatory requirements.
Starlink, on the other hand, utilizes a subscription-based pricing model. Users pay a fixed monthly fee for a specific level of service, regardless of their actual usage. This model provides predictable and stable costs, making it suitable for organizations with consistent bandwidth requirements.
As Cloud and Starlink continue to shape the future of connectivity in 2024, it’s crucial to explore the latest advancements in Starlink’s technology. Dive deeper into the Starlink 2024 Next-Generation Internet Features to gain insights into its enhanced speed, latency, and coverage capabilities.
Understanding these innovations will provide a comprehensive view of how Cloud and Starlink are revolutionizing connectivity, empowering individuals and businesses alike to unlock new possibilities in the digital landscape.
Cost-Effectiveness, Cloud vs Starlink: Revolutionizing Connectivity in 2024
The cost-effectiveness of Cloud and Starlink depends on the specific needs and usage patterns of the user. For organizations with unpredictable bandwidth requirements, the pay-as-you-go model of Cloud services can offer cost savings compared to the fixed subscription fees of Starlink.
Conversely, for organizations with consistent bandwidth needs, Starlink’s subscription model can provide a more cost-effective solution, as they can avoid paying for unused capacity.
Last Recap
As we stand on the cusp of 2024, Cloud and Starlink stand ready to usher in a new era of connectivity. Their combined potential to transform industries, bridge digital divides, and empower individuals is truly awe-inspiring. As these technologies continue to evolve and mature, we can expect even more groundbreaking applications and advancements that will shape the future of our digital world.
Quick FAQs
What is the key difference between Cloud and Starlink?
Cloud refers to computing services delivered over the internet, while Starlink is a satellite-based internet service.
Which technology offers faster speeds?
Starlink has the potential to offer higher speeds than traditional cloud-based services due to its low latency and direct connection to satellites.
Is Starlink available everywhere?
Starlink is currently expanding its coverage, but it is not yet available in all regions.